Aug 31, 2025
Introduction
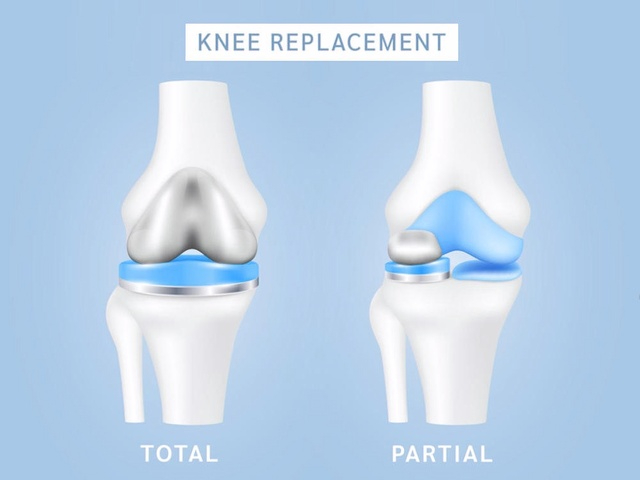
Knee replacement surgery has become one of the most common and successful orthopedic procedures worldwide. For patients suffering from severe knee pain due to osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or traumatic injuries, two main options are available: Total Knee Replacement (TKA) and Partial Knee Replacement (UKA, also called Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty).
Although both involve the implantation of a knee prosthesis, their scope, surgical techniques, recovery times, and long-term outcomes differ significantly. Understanding these differences can help patients and surgeons make the most appropriate choice.
What Is Total Knee Replacement (TKA)?
In Total Knee Replacement, the damaged cartilage and bone from all three compartments of the knee joint (medial, lateral, and patellofemoral) are removed. An artificial prosthesis made of metal and polyethylene components replaces the entire joint surface.
Coverage: Whole knee joint
Implant: Femoral component, tibial component, and patellar button (optional)
Indications: Severe arthritis affecting multiple compartments, major deformities, or instability
What Is Partial Knee Replacement (UKA)?
In Partial Knee Replacement, only the damaged part of the knee (usually the medial compartment) is replaced with a smaller prosthesis, while the healthy bone, cartilage, and ligaments remain intact.
Coverage: Only one compartment (medial, lateral, or patellofemoral)
Implant: Smaller femoral and tibial components
Indications: Early-stage osteoarthritis, pain localized to one side of the knee, preserved ligaments
Key Differences Between TKA and UKA
Feature
Total Knee Replacement (TKA)
Partial Knee Replacement (UKA)
Surgical Scope
Entire knee joint
Single compartment only
Implant Size
Larger prosthesis
Smaller prosthesis
Bone Preservation
More bone removed
More natural bone preserved
Recovery
Longer rehabilitation
Faster recovery, less pain
Indications
Severe arthritis, deformity
Early-stage arthritis, localized damage
Longevity
15–20 years
10–15 years (may convert to TKA later)
Pros and Cons
Advantages of TKA
Effective for severe or advanced arthritis
Reliable long-term outcomes
Suitable for patients with deformity or ligament damage
Advantages of UKA
Less invasive, quicker recovery
More natural knee motion
Lower blood loss during surgery
Limitations
TKA: Longer rehabilitation, more bone resection
UKA: Not suitable if multiple compartments are damaged; higher risk of revision to TKA
Conclusion
Both Total Knee Replacement and Partial Knee Replacement are proven solutions for knee arthritis, but their suitability depends on the extent of joint damage and patient condition.
TKA offers a complete solution for advanced cases, ensuring long-term durability.
UKA provides a less invasive option for patients with localized arthritis, allowing faster recovery and more natural knee function.
When choosing between the two, patients should consult with their orthopedic surgeon, considering factors like age, activity level, and overall knee health.
Read More